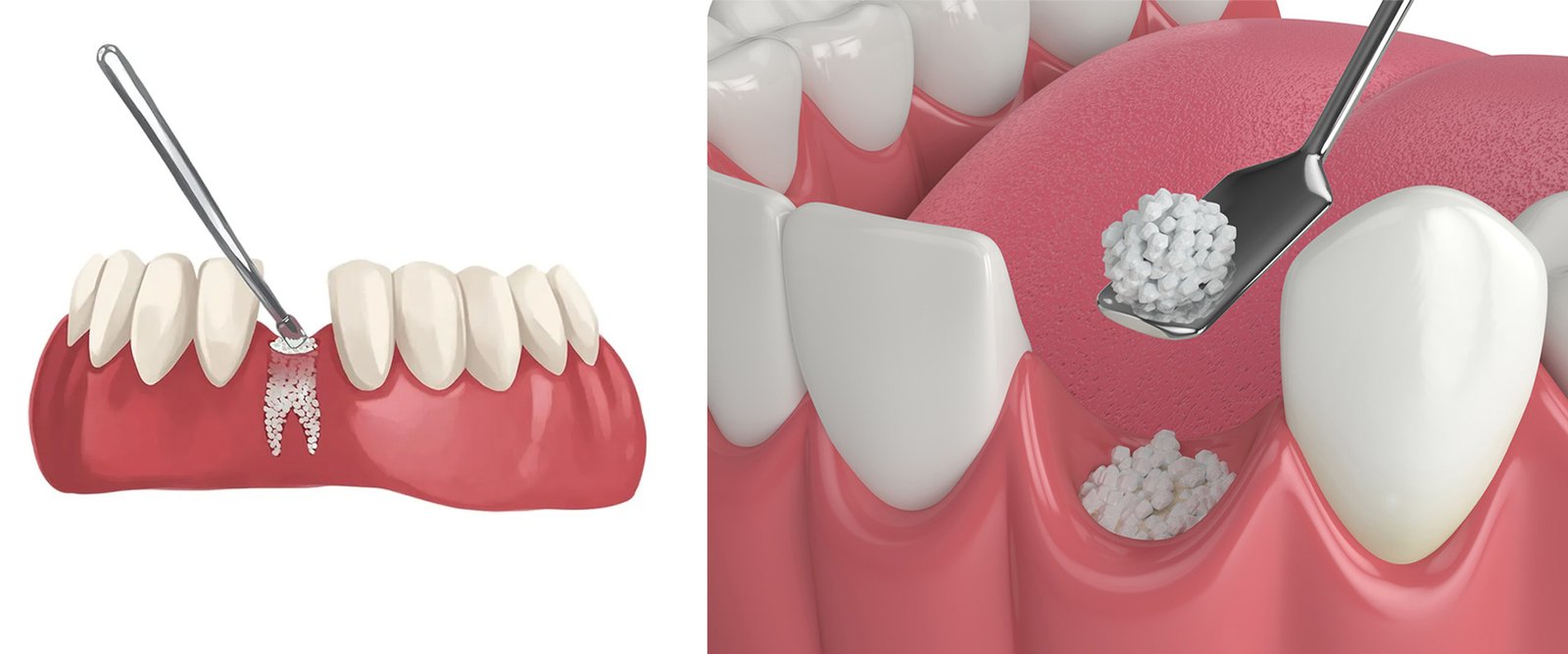
Bone Grafting
Bone grafting is a surgical procedure used to repair or rebuild bones through the transplantation of bone tissue. This technique is commonly employed in situations where bones are damaged due to trauma, disease, or congenital defects, and in cases where there is a need to facilitate bone healing and growth.
How Bone Grafting Works
Bone grafting involves taking bone from a donor site and transplanting it to the area needing repair. The graft can come from several sources:
- Autografts: Bone taken from another part of the patient’s own body.
- Allografts: Bone sourced from a deceased donor or a cadaver, which is processed and stored in a tissue bank.
- Synthetic options: Man-made materials that mimic the properties of natural bone.
Types of Bone Grafts
- Autograft: The most effective type of graft, as it uses the patient’s own bone, eliminating the risk of graft rejection and disease transmission.
- Allograft: Commonly used for its availability and convenience, although there is a slight risk of immune response or disease transmission.
- Xenograft: Bone taken from another species, such as bovine, which is treated and sterilized to be compatible with human tissue.
- Synthetic Grafts: Made from materials like ceramics, bioactive glass, or polymers, these grafts are designed to support bone regeneration and provide a scaffold for new bone growth.
Applications of Bone Grafting
Bone grafting is utilized in various medical fields, including:
- Orthopedic Surgery: To repair fractures or bone defects caused by trauma or conditions like osteoporosis.
- Dental Implants: To rebuild bone in the jaw that has deteriorated, ensuring a stable foundation for dental implants.
- Spinal Fusion: To join two or more vertebrae, alleviating pain caused by spinal instability or degenerative conditions.
- Bone Cancer Treatment: To replace bone removed during the surgical treatment of bone tumors.
The Bone Grafting Procedure
- Preparation: The surgical site is prepared, and the area for bone harvesting (in the case of autografts) is selected.
- Harvesting the Graft: Bone tissue is carefully harvested from the donor site.
- Placing the Graft: The harvested bone is shaped and placed in the area needing repair, often secured with pins, plates, or screws.
- Healing Process: Over time, the grafted bone integrates with the existing bone, supported by new bone growth stimulated by the graft.
Recovery and Healing
Recovery from a bone grafting procedure varies depending on the complexity of the surgery and the patient’s overall health. Postoperative care may include:
- Pain management.
- Physical therapy.
- Follow-up appointments to monitor healing progress.
Bone grafting is a vital procedure in modern medicine, offering solutions to complex bone-related issues and enhancing the quality of life for many patients.
Contact Us
For more information about bone grafting or to schedule a consultation, please contact our office. Our experienced team is here to help you achieve optimal bone health and recovery.



